Flame cutting
Flame cutting
Prior to flame cutting operations on rails, they should be cleaned from rust, scale, grease and dirt. The cutting torch should be mounted perpendicular to the rail on a carriage, so that there is a consistent distance away from the rail and the cleanliness of the flame cut is guaranteed.
The flame cut can be done with a flame cutting gauge, thus a 90° cut to the rail is possible.
If rails with 880 N/mm² minimum tensile strength are installed then the rails should be warmed before the start of flame cutting. The rail should be warmed over a length of 1 m around the place to be cut (to about 50°C). It is recommended that the rail directly adjacent to the place to be cut should be heated over a length of 10 cm to the left and right to approx. 400°C. This should be checked with thermochromic pins. If this warm-up is not carried out, a hard martensite microstructure will be formed on the rail ends. Later, when the treated rails are in service there may be a structure separation or even a crack formation (broken rail).
The burning out of holes in the rail web for fishplate bolts is prohibited and, therefore, is strictly forbidden. The different loadings (bending and tensile stress), may cause longitudinal and transverse cracks which can lead to additional hazards.
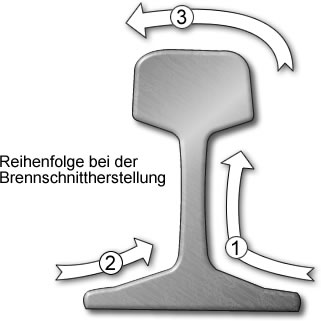
Sequence in flame cutting operations:
You can find suitable specialist literature to the topic here:
The Basic Principles of Mechanised Track Maintenance
This book is dedicated to the many people involved in the day to day planning and performance of track maintenance activities. Providing a practical approach to everyday challenges in mechanised track maintenance, it is not just intended as a theoretical approach to the track system.
Railways aim at transporting people and freight safely, rapidly, regularly, comfortably and on time from one place to another. This book is directed to track infrastructure departments contributing to the above objective by ensuring the track infrastructure’s reliability, availability, maintainability and safety – denoted by the acronym RAMS. Regular, effective and affordable track maintenance enable RAMS to be achieved.